Complete NCERT Solutions Guide
Access step-by-step solutions for all NCERT textbook questions
Welcome to the Chapter 10 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions page. Here, we provide detailed question answers for Chapter 10 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. The page is designed to help students gain a thorough understanding of the concepts related to natural resources, their classification, and sustainable development.
Our solutions explain each answer in a simple and comprehensive way, making it easier for students to grasp key topics Haloalkanes and Haloarenes and excel in their exams. By going through these Haloalkanes and Haloarenes question answers, you can strengthen your foundation and improve your performance in Class 12 Chemistry. Whether you’re revising or preparing for tests, this chapter-wise guide will serve as an invaluable resource.
In the presence of sulphuric acid (H2SO4), KI produces HI
2KI + H2SO4 → 2KHSO4 + 2HI
Since H2SO4 is an oxidizing agent, it oxidizes HI (produced in the reaction to I2).
2HI + H2SO4 → I2 + SO2 + H2O
As a result, the reaction between alcohol and HI to produce alkyl iodide cannot occur. Therefore, sulphuric acid is not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI. Instead, a non-oxidizing acid such as H3PO4 is used.
There are four different dihalogen derivatives of propane. The structures of these derivatives are shown below.

(i) To have a single monochloride, there should be only one type of H-atom in the isomer of the alkane of the molecular formula C5H12. This is because, replacement of any H-atom leads to the formation of the same product. The isomer is neopentane.

Neopentane
(ii) To have three isomeric monochlorides, the isomer of the alkane of the molecular formula C5H12 should contain three different types of H-atoms.
Therefore, the isomer is n-pentane. It can be observed that there are three types of H atoms labelled as a, b and c in n-pentane.

(iii) To have four isomeric monochlorides, the isomer of the alkane of the molecular formula C5H12 should contain four different types of H-atoms. Therefore, the isomer is 2-methylbutane. It can be observed that there are four types of H-atoms labelled as a, b, c, and d in 2-methylbutane.

(i)

For alkyl halides containing the same alkyl group, the boiling point increases with an increase in the atomic mass of the halogen atom.
Since the atomic mass of Br is greater than that of Cl, the boiling point of bromomethane is higher than that of chloromethane.
Further, for alkyl halides containing the same alkyl group, the boiling point increases with an increase in the number of halides. Therefore, the boiling point of Dibromomethane is higher than that of chloromethane and bromomethane, but lower than that of bromoform.
Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the order of their increasing boiling points as:
Chloromethane < Bromomethane < Dibromomethane < Bromoform.
(ii)

For alkyl halides containing the same halide, the boiling point increases with an increase in the size of the alkyl group. Thus, the boiling point of 1-chlorobutane is higher than that of isopropyl chloride and 1-chloropropane.
Further, the boiling point decreases with an increase in branching in the chain. Thus, the boiling point of isopropyl alcohol is lower than that of 1-chloropropane.
Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their boiling points as:
Isopropyl chloride < 1-Chloropropane < 1-Chlorobutane
(i)

2-bromobutane is a 2° alkylhalide whereas 1-bromobutane is a 1° alkyl halide. The approaching of nucleophile is more hindered in 2-bromobutane than in 1-bromobutane. Therefore, 1-bromobutane reacts more rapidly than 2-bromobutane by an SN2 mechanism.
(ii)

2-Bromobutane is 2° alkylhalide whereas 2-bromo-2-methylpropane is 3° alkyl halide. Therefore, greater numbers of substituents are present in 3° alkyl halide than in 2° alkyl halide to hinder the approaching nucleophile. Hence, 2-bromobutane reacts more rapidly than 2-bromo-2-methylpropane by an SN2 mechanism.
(iii)

Both the alkyl halides are primary. However, the substituent -CH3 is at a greater distance to the carbon atom linked to Br in 1-bromo-3-methylbutane than in 1-bromo-2-methylbutane. Therefore, the approaching nucleophile is less hindered in case of the former than in case of the latter. Hence, the former reacts faster than the latter by SN2 mechanism.
(i)

SN1 reaction proceeds via the formation of carbocation. The alkyl halide (I) is 3° while (II) is 2°. Therefore, (I) forms 3° carbocation while (II) forms 2° carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, faster is the rate of SN1 reaction. Since 3° carbocation is more stable than 2° carbocation. (I), i.e. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane, undergoes faster SN1 reaction than (II) i.e., 3-chloropentane.
(ii)

The alkyl halide (I) is 2° while (II) is 1°. 2° carbocation is more stable than 1° carbocation. Therefore, (I), 2-chloroheptane, undergoes faster SN1 reaction than (II), 1-chlorohexane.

Saytzeff's rule implies that in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to a doubly bonded carbon atoms is preferably produced. Therefore, alkene (I) i.e., 2-methylbut-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
(iii)

2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.

According to Saytzeff's rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atom is preferably formed. Hence, alkene (I) i.e., 3,4,4-trimethylpent-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
(i)

In chlorobenzene, the Cl-atom is linked to a sp2 hybridized carbon atom. In cyclohexyl chloride, the Cl-atom is linked to a sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Now, sp2 hybridized carbon has more s-character than sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Therefore, the former is more electronegative than the latter. Therefore, the density of electrons of C - Cl bond near the Cl-atom is less in chlorobenzene than in cydohexyl chloride.
Moreover, the - R effect of the benzene ring of chlorobenzene decreases the electron density of the C - Cl bond near the Cl-atom. As a result, the polarity of the C - Cl bond in chlorobenzene decreases. Hence, the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(ii) To be miscible with water, the solute-water force of attraction must be stronger than the solute-solute and water-water forces of attraction. Alkyl halides are polar molecules and so held together by dipole-dipole interactions. Similarly, strong H-bonds exist between the water molecules. The new force of attraction between the alkyl halides and water molecules is weaker than the alkyl halide-alkyl halide and water-water forces of attraction. Hence, alkyl halides (though polar) are immiscible with water.
(iii) Grignard reagents are very reactive. In the presence of moisture, they react to give alkanes.

Therefore, Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Uses of Freon - 12
Freon-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane, CF2Cl2) is commonly known as CFC. It is used as a refrigerant in refrigerators and air conditioners. It is also used in aerosol spray propellants such as body sprays, hair sprays, etc. However, it damages the ozone layer. Hence, its manufacture was banned in the United States and many other countries in 1994.
Uses of DDT
DDT (p, p-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) is one of the best known insecticides. It is very effective against mosquitoes and lice. But due its harmful effects, it was banned in the United States in 1973.
Uses of carbontetrachloride (CCl4)
(i) It is used for manufacturing refrigerants and propellants for aerosol cans.
(ii) It is used as feedstock in the synthesis of chlorofluorocarbons and other chemicals.
(iii) It is used as a solvent in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products.
(iv) Until the mid 1960's, carbon tetrachloride was widely used as a cleaning fluid, a degreasing agent in industries, a spot reamer in homes, and a fire extinguisher.
Uses of iodoform (CHI3)
Iodoform was used earlier as an antiseptic, but now it has been replaced by other formulations-containing iodine-due to its objectionable smell. The antiseptic property of iodoform is only due to the liberation of free iodine when it comes in contact with the skin.
The given reaction is:

The given reaction is an SN2 reaction. In this reaction, CN - acts as the nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom to which Br is attached. CN - ion is an ambident nucleophile and can attack through both C and N. In this case, it attacks through the C-atom.

(i)

An SN2 reaction involves the approaching of the nucleophile to the carbon atom to which the leaving group is attached. When the nucleophile is sterically hindered, then the reactivity towards SN2 displacement decreases. Due to the presence of substituents, hindrance to the approaching nucleophile increases in the following order.
1-Bromopentane < 2-bromopentane < 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
Hence, the increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement is:
2-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 2-Bromopentane < 1-Bromopentane
(ii)

Since steric hindrance in alkyl halides increases in the order of 1° < 2° < 3°, the increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement is 3° < 2° < 1°.
Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their reactivity towards SN2 displacement as:
2-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane
[2-Bromo-3-methylbutane is incorrectly given in NCERT]
(iii)

The steric hindrance to the nucleophile in the SN2 mechanism increases with a decrease in the distance of the substituents from the atom containing the leaving group. Further, the steric hindrance increases with an increase in the number of substituents. Therefore, the increasing order of steric hindrances in the given compounds is as below:
1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane
< 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane
Hence, the increasing order of reactivity of the given compounds towards SN2 displacement is:
1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane < 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-3- methylbutane < 1-Bromobutane

p-Dichlorobenzene is more symmetrical than o-and m-isomers. For this reason, it fits more closely than o-and m-isomers in the crystal lattice. Therefore, more energy is required to break the crystal lattice of p-dichlorobenzene. As a result, p-dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point and lower solubility than o-and m-isomers.
In an aqueous solution, KOH almost completely ionizes to give OH - ions. OH - ion is a strong nucleophile, which leads the alkyl chloride to undergo a substitution reaction to form alcohol.
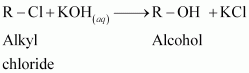
On the other hand, an alcoholic solution of KOH contains alkoxide (RO - ) ion, which is a strong base. Thus, it can abstract a hydrogen from the β-carbon of the alkyl chloride and form an alkene by eliminating a molecule of HCl.

OH - ion is a much weaker base than RO - ion. Also, OH - ion is highly solvated in an aqueous solution and as a result, the basic character of OH - ion decreases. Therefore, it cannot abstract a hydrogen from the β-carbon.
There are two primary alkyl halides having the formula, C4H9Br. They are n - bulyl bromide and isobutyl bromide.

Therefore, compound (a) is either n-butyl bromide or isobutyl bromide.
Now, compound (a) reacts with Na metal to give compound (b) of molecular formula, C8H18, which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide reacts with Na metal. Hence, compound (a) must be isobutyl bromide.

Thus, compound (d) is 2, 5-dimethylhexane.
It is given that compound (a) reacts with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Hence, compound (b) is 2-methylpropene.

Also, compound (b) reacts with HBr to give compound (c) which is an isomer of (a). Hence, compound (c) is 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.

(i) When n - butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH, the formation of but - l - ene takes place. This reaction is a dehydrohalogenation reaction.

(ii) When bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether, phenylmagnesium bromide is formed.

(iii) Chlorobenzene does not undergo hydrolysis under normal conditions. However, it undergoes hydrolysis when heated in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623 K and a pressure of 300 atm to form phenol.

(iv) When ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH, it undergoes hydrolysis to form ethanol.

(v) When methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, ethane is formed. This reaction is known as the Wurtz reaction.

(vi) When methyl chloride is treated with KCN, it undergoes a substitution reaction to give methyl cyanide.


CCl4 is a symmetrical molecule. Therefore, the dipole moments of all four C-Cl bonds cancel each other. Hence, its resultant dipole moment is zero.
As shown in the above figure, in CHCl3, the resultant of dipole moments of two C-Cl bonds is opposed by the resultant of dipole moments of one C-H bond and one C-Cl bond. Since the resultant of one C-H bond and one C-Cl bond dipole moments is smaller than two C-Cl bonds, the opposition is to a small extent. As a result, CHCl3 has a small dipole moment of 1.08 D.
On the other hand, in case of CH2Cl2, the resultant of the dipole moments of two C-Cl bonds is strengthened by the resultant of the dipole moments of two C-H bonds. As a result, CH2Cl2 has a higher dipole moment of 1.60 D than CHCl3 i.e., CH2Cl2 has the highest dipole moment.
Hence, the given compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their dipole moments as:
CCl4 < CHCl3 < CH2Cl2
A hydrocarbon with the molecular formula, C5H10 belongs to the group with a general molecular formula CnH2n. Therefore, it may either be an alkene or a cycloalkane.
Since hydrocarbon does not react with chlorine in the dark, it cannot be an alkene. Thus, it should be a cycloalkane.
Further, the hydrocarbon gives a single monochloro compound, C5H9Cl by reacting with chlorine in bright sunlight. Since a single monochloro compound is formed, the hydrocarbon must contain H-atoms that are all equivalent. Also, as all H-atoms of a cycloalkane are equivalent, the hydrocarbon must be a cycloalkane. Hence, the said compound is cyclopentane.

There are four isomers of the compound having the formula C4H9Br. These isomers are given below.

Ambident nucleophiles are nucleophiles having two nucleophilic sites. Thus, ambident nucleophiles have two sites through which they can attack.
For example, nitrite ion is an ambident nucleophile.

Nitrite ion can attack through oxygen resulting in the formation of alkyl nitrites. Also, it can attack through nitrogen resulting in the formation of nitroalkanes.

(i) In the SN2 mechanism, the reactivity of halides for the same alkyl group increases in the order. This happens because as the size increases, the halide ion becomes a better leaving group.
R-F << R-Cl < R-Br < R-I
Therefore, CH3I will react faster than CH3Br in SN2 reactions with OH-.
(ii)

The SN2 mechanism involves the attack of the nucleophile at the atom bearing the leaving group. But, in case of (CH3)3CCl, the attack of the nucleophile at the carbon atom is hindered because of the presence of bulky substituents on that carbon atom bearing the leaving group. On the other hand, there are no bulky substituents on the carbon atom bearing the leaving group in CH3Cl. Hence, CH3Cl reacts faster than (CH3)3CCl in SN2 reaction with OH-.
Join thousands of students who have improved their academic performance with our comprehensive study resources.